by Zach Pinto
Director, Carbon & Ecosystem Service Markets
In late 2015, many governments adopted the Paris Agreement – a legally binding, international treaty on greenhouse gas emissions. Since then, corporations and NGOS have joined governments to develop targets and strategies to limit environmental impacts. Now several years into the treaty, recent articles and analyses indicate that, collectively, we aren’t on track to make the changes needed.
Sustainability Commitments
To date, 341 food and agriculture companies have committed to and are engaging in science-based targets to advance sustainability and lower their environmental footprints.
Within those commitments, targets around Scope 3 emissions offer the greatest opportunity for reductions and impact. Scope 3 emissions are environmental externalities that fall outside of a company’s direct control, typically within their upstream or downstream supply chains.
For many food, feed, fuel, and fiber companies across the globe, reducing environmental impacts at the farm level is imperative for making progress toward these targets.

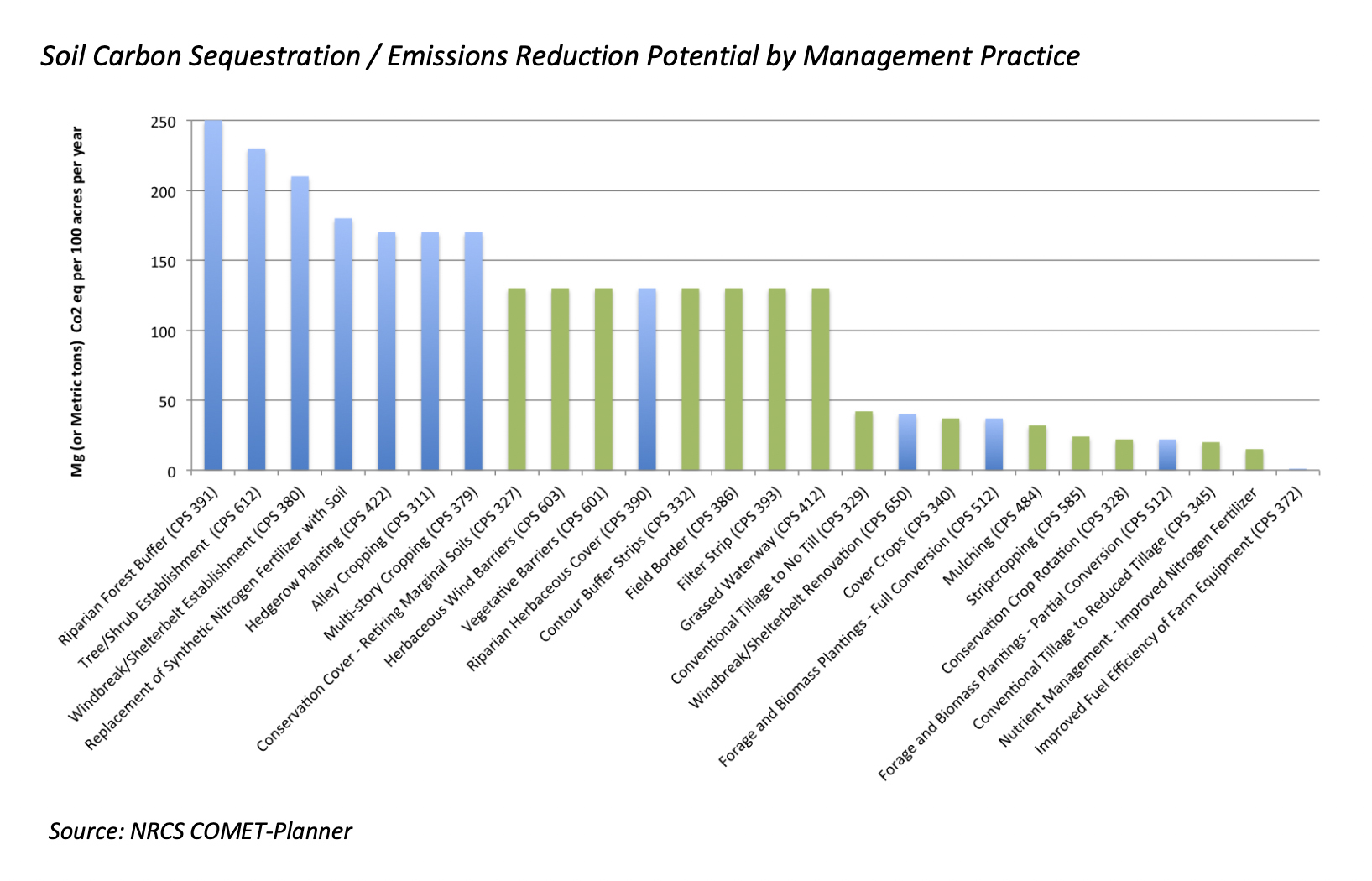
Solutions within Agriculture
Promising research shows that solutions exist within agriculture to accelerate progress and generate environmental benefit. From carbon sequestration, to improved water quality and usage, to enhanced biodiversity, these solutions can be scaled for positive global impacts.
The good news is, much of the great work our industry is doing to inset its impacts – carbon programs, ecosystem markets, NRCS programs, USDA Partnerships for Climate Smart Commodities – can count as progress toward these targets. The key, of course, is making sure all of this work is measurable, verifiable, and scalable – and ensuring that the changes work for farmers and ranchers – both agronomically and economically.
Here are three ways to strengthen your sustainability strategy and start unlocking the potential within agriculture:
- Plan your strategy: Clarify what your supply shed looks like and outline your path forward. What are the most effective ways to drive change, measure progress, and reward farmers in the process?
- Partner with farmers: Farmers know how to farm, but adoption of regenerative practices is not a one-strategy-fits-all approach – cover crops don’t work for every farm, for example. Once you know where to focus, make sure you consult growers in the region to ensure you create interventions that work for their farm-specific conditions, make agronomic sense, and prove to be economically viable.
- Implement on the ground: Run pilots to test strategies and eventually scale them into full interventions. Ensure practices and outcomes align with leading public cost share programs and private ecosystem service markets that pay growers and count towards your targets.
Read more about how AgSpire can provide strategic guidance and implementation assistance to advance your sustainability goals: Our Services
Learn More
To showcase the great work going on in our industry, incentivize continuous improvement, and reward farmers for the positive practices they implement, many companies worldwide have set rigorous, protocol-based targets. These include:
- Science-Based Targets: These targets define how quickly and by how much companies should reduce their environmental impacts, based on the best available science, to ensure that global goals such as the Paris Agreement or the Global Biodiversity Framework are met. Science-based targets for greenhouse gas emissions must be validated by the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi), and Science-based targets for water, land, and biodiversity must be validated by the Science Based Targets Network (SBTN).
- Net Zero Targets: Net Zero Targets are science-based targets that set the standard for how a company can credibly reduce their carbon footprint to net zero (when the amount of all greenhouse gases a company emits equals the amount it removes from the atmosphere) by 2050.
Additional Reading and Citations:
Soil Health and Carbon Sequestration in US Croplands: A Policy Analysis – https://food.berkeley.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/GSPPCarbon_03052016_FINAL.pdf
Cover Crops, No-Till Increase Carbon Gains in Soil – https://www.no-tillfarmer.com/articles/9818-cover-crops-no-till-increase-carbon-gains-in-soil
Negative Emissions Technologies and Reliable Sequestration – https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/25259/negative-emissions-technologies-and-reliable-sequestration-a-research-agenda
About the Author
ZACH PINTO
Director of Carbon & Ecosystem Service Markets
Zach promotes company strategy and client success by assisting industry groups, food and ag companies, and farmers on their sustainability goals. Zach has worked on carbon issues for stakeholders across the agriculture value chain and in a wide array of commodities, developing expertise in farm-level carbon accounting, MRV platform usage, voluntary and compliance market schemes, science-based targets, ESG reporting, and strategic planning.